Understanding Essential DNS Record Types for Web Administrators
Introduction
The Domain Name System (DNS) acts as the backbone of the internet, enabling humans to access websites using user-friendly domain names instead of hard-to-remember IP addresses. As a web administrator or developer, understanding key DNS record types is crucial for managing domains, emails, and servers efficiently. In this blog, we will break down the most essential DNS records, their functions, and how they work.
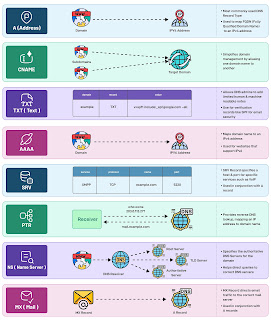
1. A (Address) Record
• Purpose: Maps a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) to an IPv4 address.
• Usage: The most common DNS record used for connecting domains to servers.
• Example:
example.com -> 192.168.1.1
2. CNAME (Canonical Name) Record
• Purpose: Simplifies domain management by aliasing one domain name to another.
• Usage: Redirects subdomains or secondary domains to a target domain without managing multiple IP addresses.
• Example:
www.example.com -> example.com
3. TXT (Text) Record
• Purpose: Stores human- or machine-readable text data. Commonly used for verification and security purposes.
• Usage: Used for SPF records (email security), domain verification (Google, Microsoft), or adding metadata.
• Example:
v=spf1 include:_spf.google.com -all
4. AAAA Record
• Purpose: Maps a domain name to an IPv6 address (instead of IPv4).
• Usage: Important for websites or services supporting IPv6.
• Example:
example.com -> 2001:db8::1
5. SRV (Service) Record
• Purpose: Specifies a host and port for specific services like VoIP or instant messaging




No comments:
Post a Comment